- Updated on August 13, 2020
![]() By Dr. Artour Rakhimov, Alternative Health Educator and Author
By Dr. Artour Rakhimov, Alternative Health Educator and Author
- Medically Reviewed by Naziliya Rakhimova, MD
Learning the Buteyko method by modules
Module 8-A. Restrictions, side effects, limits, and temporary contraindications
Brain traumas and acute bleeding injuries
It is possible and relatively easy to treat and heal traumatic injuries for the head and brain with breathing retraining. At over 30 s morning CP, the immune launches active repair of cells and tissues of the head as well as nerve cells of the brain. However, this treatment cannot be started during acute episodes or stages when bleeding is present or possible since tissues are not strong enough to withstand increased blood flow due to higher CO2 during breathing exercises (Buteyko, yoga pranayama, Frolov or DIY devices).
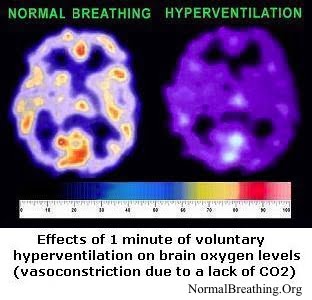 Hyperventilation is a normal and useful reaction to bleeding injuries. Reduced CO2 content in the blood decreases blood flow to vital organs and other tissues of the human body. This prevents excessive blood losses and can save one’s life. Emergency professionals even coined a term “permissive hyperventilation” that is used for people with, for example, brain trauma.
Hyperventilation is a normal and useful reaction to bleeding injuries. Reduced CO2 content in the blood decreases blood flow to vital organs and other tissues of the human body. This prevents excessive blood losses and can save one’s life. Emergency professionals even coined a term “permissive hyperventilation” that is used for people with, for example, brain trauma.
Therefore, in cases of acute brain traumas and bleeding injuries, it is not a wise idea to apply any breathing technique that increases CO2 and blood flow (perfusion) to body organs.
Later, when bleeding ceased, it is possible to follow the common program of breathing retraining (if there are no any other restrictions) and get all those amazing health benefits that come with normal breathing and high body oxygen levels.
– This page in Spanish: Traumas cerebrales y lesiones hemorrágicas agudas y ejercicios de respiración.
Related pages:
– Body and brain oxygen content: Why it is hard to measure O2 with devices and a solution
– Brain diseases that are treated with breathing retraining with great results
– Increase brain oxygen with this simple breathing exercise
– How to calm nerves using the reduced breathing exercise in 1-2 minutes
– CO2: most potent sedative and tranquilizer of nerve cells.

